Understanding payroll taxes is essential to running a compliant and financially healthy business. Knowing how employment taxes work helps you make smarter financial decisions and avoid costly penalties, whether you’re managing a small team or a growing organization.
Payroll tax accuracy matters more than ever. New tax rates, updated Social Security and Medicare taxes, and evolving wage base limits mean you can’t afford to rely on outdated information. It’s imperative to stay updated to avoid potential penalties and ensure compliance.
This guide will walk you through the main types of payroll taxes, explain how employers and employees share responsibility, and give you practical tips to reduce your tax burden while staying compliant.
What Are Payroll Taxes?
Payroll taxes are the required amounts withheld from employee paychecks and paid by employers to fund key federal and state programs. These include Social Security and Medicare taxes, which support retirees, people with disabilities, and healthcare for older Americans.
As an employer, you’re also responsible for federal unemployment taxes (FUTA) and possibly state unemployment taxes (SUTA), which fund unemployment benefits for eligible workers. These contributions are vital—not only to maintain compliance but also to support the larger workforce ecosystem that your business depends on.
Simply put, payroll taxes are your way of contributing to the programs that protect your employees and strengthen your business community. Your contributions play a vital role in supporting retirees, people with disabilities, and healthcare for older Americans.
The Main Types of Payroll Taxes
1. Federal Income Tax
Every pay period, you’re required to withhold federal income tax from your employees’ wages. The amount depends on the details they provide on Form W-4, including marital status, dependents, and any additional income or deductions.
Be sure to use the latest IRS withholding tables for 2025. Using outdated tax rate information can lead to over- or under-withholding, creating confusion when employees file their tax returns.
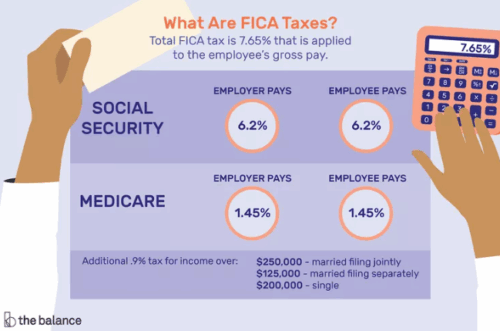
2. FICA Tax: Social Security and Medicare Taxes
The FICA tax combines two significant contributions—Social Security tax and Medicare tax—that you and your employees share equally.
Social Security Tax
- Employees pay 6.2% of their wages to the annual wage base limit, which adjusts yearly.
- You pay a matching 6.2% as the employer.
- Once employees reach the wage base limit, this tax no longer applies for the remainder of the year.
These funds support millions of Americans, so accuracy and timely deposits are crucial.
Medicare Tax
- Employees pay 1.45% of all wages, with no wage cap.
- You pay a matching 1.45%.
- High earners must also pay an Additional Medicare Tax of 0.9% on wages over $200,000 for single filers or $250,000 for joint filers.
You’re responsible for withholding the additional Medicare taxes when your employees reach that income level. Although you don’t match this extra amount, ensuring correct withholding keeps your business compliant.
Together, these Social Security and Medicare taxes represent the foundation of the U.S. social insurance system—and your contributions make it possible.
3. Federal Unemployment Tax (FUTA)
Unlike income or FICA taxes, only employers pay federal unemployment taxes. The tax rate is 6.0% on the first $7,000 of each employee’s wages.
Most employers, however, qualify for a tax credit of up to 5.4% for paying their state unemployment taxes on time—reducing your effective FUTA rate to 0.6%.
By paying this employment tax accurately, you’re helping fund unemployment benefits that support workers during transitions, layoffs, or economic shifts.
4. State and Local Payroll Taxes
Depending on where your employees work, you may also need to manage state and local payroll taxes. These can include:
- State income tax (withheld from employee wages)
- State unemployment tax (typically paid by employers)
- City or county income taxes
If you have remote employees in multiple states, take special care to identify which tax applies based on their work location, not just your headquarters.
5. Payroll Taxes for Different Employers
Your employment tax responsibilities may look a little different depending on your organization’s structure:
- Remote Teams: You must remit payroll taxes to the correct state agencies for each employee’s work location.
- Faith-Based Organizations: Ministers are typically treated as self-employed for Social Security and Medicare taxes, paying through self-employment tax.
- Nonprofits: Even though nonprofits are exempt from federal income tax, they still must withhold and pay FICA tax, federal unemployment taxes, and other applicable withholdings for paid staff.
Why Payroll Taxes Matter to You
1. Compliance and Risk Management
Late filings or incorrect calculations can lead to severe penalties from the IRS or state agencies. Staying proactive about payroll tax management helps you avoid fines and maintain compliance.
2. Employee Confidence
When employees see accurate withholdings and timely W-2s, it builds trust. Managing Social Security and Medicare taxes accurately demonstrates to your team that you value transparency and reliability.
3. Financial Control
Understanding how employers pay and how employees pay into each tax allows you to forecast your tax burden more precisely and plan for business growth without surprises.
Smart Ways to Manage Payroll Taxes
Calculate Payroll Taxes Accurately
Always use the latest IRS and SSA resources for FICA tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax calculations. Regularly update your payroll software so that every tax rate reflects current laws. Accuracy in these calculations is not just a goal, it’s a necessity.
Maintain Detailed Records
Keep accurate documentation of employee wages, withholdings, and deposits. Organized records make filing tax returns and defending your business easier during audits.
File and Pay on Time
Your deposit schedule—monthly, semi-weekly, or next-day—depends on your total tax liability. Ensure you’re filing Form 941 quarterly and Form 940 annually for FUTA. Missing deadlines, even by one day, can trigger automatic penalties.
Train Your Payroll Team
If your business manages payroll internally, train your team on annual updates to wage base limits, additional Medicare taxes, and state tax changes. Understanding which tax applies to bonuses, overtime, or fringe benefits prevents costly errors.
Audit Your Payroll
Conduct quarterly audits to verify that employers and employees are paying their respective portions of each tax accurately. Check for errors in withheld amounts from employee paychecks and verify that all deposits match your filings.
Embrace Payroll Technology
Manual payroll is risky and time-consuming. Automated payroll software—or partnering with a provider like APS—can simplify your entire process, reduce human error, and ensure compliance year-round.
Payroll Tax Highlights
Each year brings updates to employment tax thresholds and rates. Here are some common updates to be aware of:
- Social Security wage base limit increases again, meaning you’ll withhold and match 6.2% on higher wages.
- The Additional Medicare Tax thresholds remain at $200,000 for individuals and $250,000 for married couples filing jointly.
- The FUTA tax rate stays at 6.0%, with most employers receiving the 5.4% tax credit for timely state payments.
- IRS guidance on Form W-4 emphasizes the importance of accurate withholding for variable income earners.
Staying informed about these changes helps you manage payroll proactively, rather than reacting at year-end.
How APS Payroll Can Help
If managing multiple tax rates and employment tax filings feels overwhelming, APS can help. Our payroll platform automates calculations, deposits, and compliance monitoring—so you can focus on running your business. Here’s how APS supports you:
✅ Automated Accuracy: APS automatically calculates FICA, Social Security, and Medicare tax using the current tax rate and wage base limit data.
✅ Effortless Filings: Our tax team prepares and files Form 941, Form 940, and other required tax returns on time.
✅ Compliance Confidence: We stay updated on every rule change, ensuring the correct tax applies to every transaction.
✅ Employee Self-Service: Your team can access pay stubs, W-2s, and tax returns anytime.
✅ Dedicated Support: You get a consistent team of experts—not a call center—ready to answer your payroll tax questions.
With APS, you’ll streamline your employment tax process, lower your tax burden, and eliminate the stress of managing compliance manually.
Understanding Payroll Taxes Is Key to Your Success
Understanding how employees pay and how employers pay into Social Security and Medicare taxes, federal unemployment taxes, and other programs is crucial for protecting your business and its employees.
By managing payroll taxes proactively, you’ll save time, minimize risk, and strengthen employee trust—all while keeping your business on solid financial ground.
👉 Learn how APS Payroll can simplify payroll tax management for your organization.
Sources
- Payroll Tax | Tax Foundation
- Topic no. 751 | IRS
- Medicare Wages: Definition, How They’re Taxed, Limits, and Rates | Investopedia
- Topic no. 759 | IRS
- Payroll Taxes: What Are They and What Do They Fund? | Peter G. Peterson Foundation
- About Form 941 | IRS
- Social Security Tax Limit for 2025 | SmartAsset
- Understanding Employment Taxes | IRS